
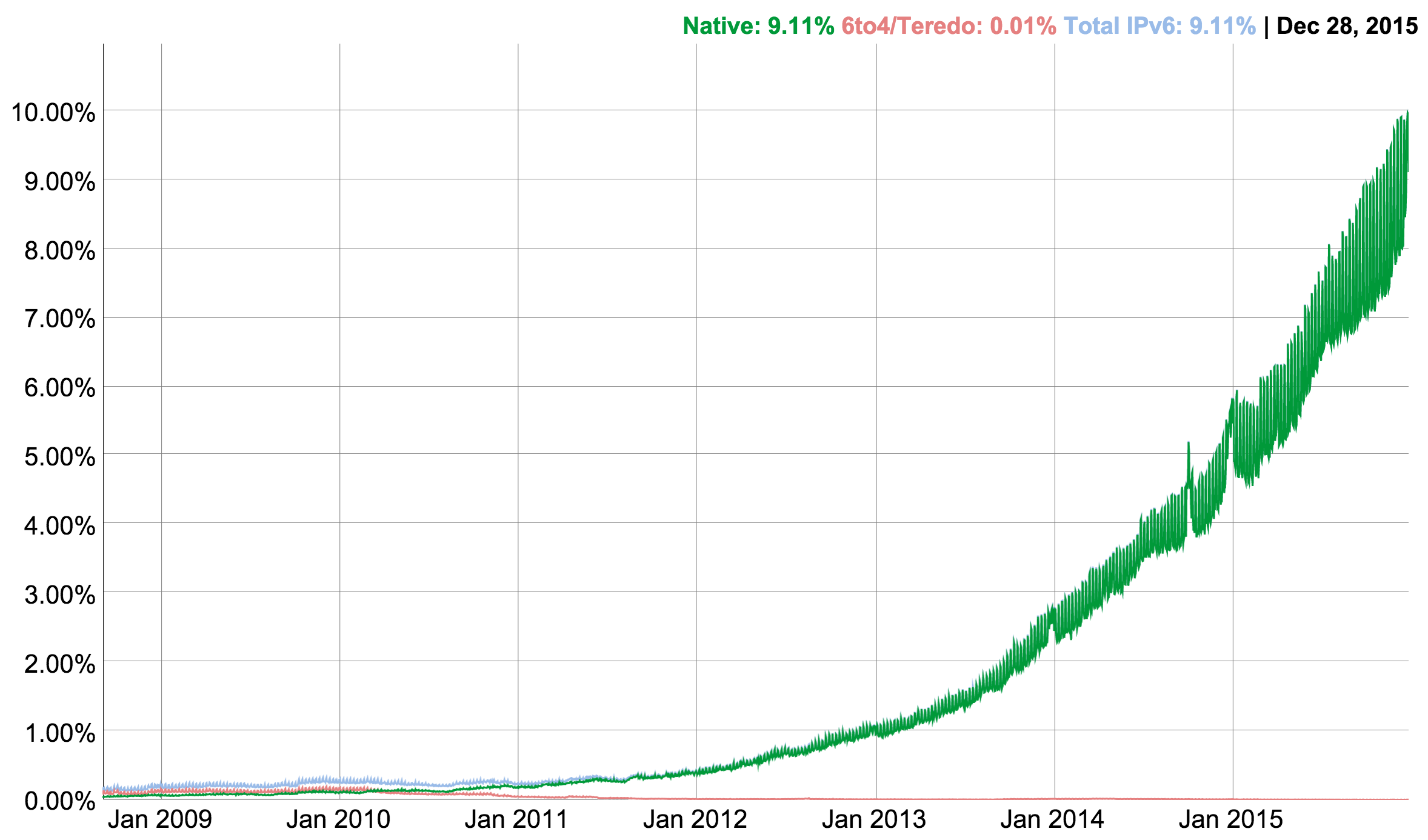
My latest Ars Technica IPv6 story is about IPv6 celebrating its 20th birthday and that it has reached 10% deployment at the end of 2015.
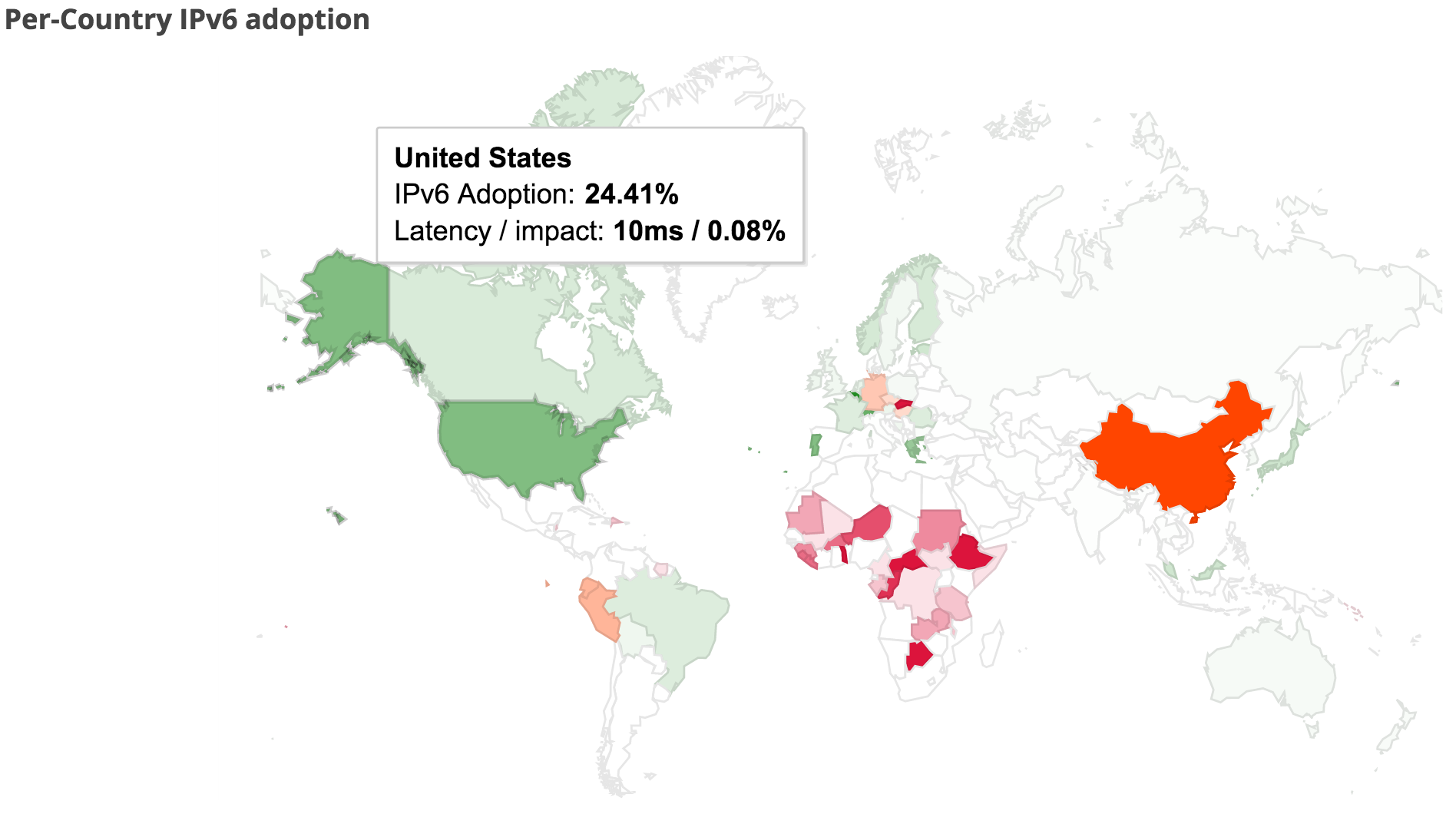
And the US is doing very well with almost 25% IPv6 deployment:
Read the article - posted 2016-01-04
Mijn recentste IPv6-verhaal voor Ars Technica gaat over het feit dat IPv6 afgelopen maand z'n twintigste verjaardag vierde: in december 1995 is RFC 1883, de eerste IPv6-specificatie, gepubliceerd. Een ander gedenkwaardig feit is dat volgens de statistieken van Google nu 10% van de internetgebruikers de beschikking heeft over IPv6.

In de Verenigde Staten is dit zelfs al bijna 25%:

Dit ondanks het feit dat de VS lange tijd nogal achter liep. Nederland daarentegen ging goed van start, met name dankzij XS4ALL, dat er vroeg bij was. Maar we zitten nu in de middenmoot met nog geen 4%:
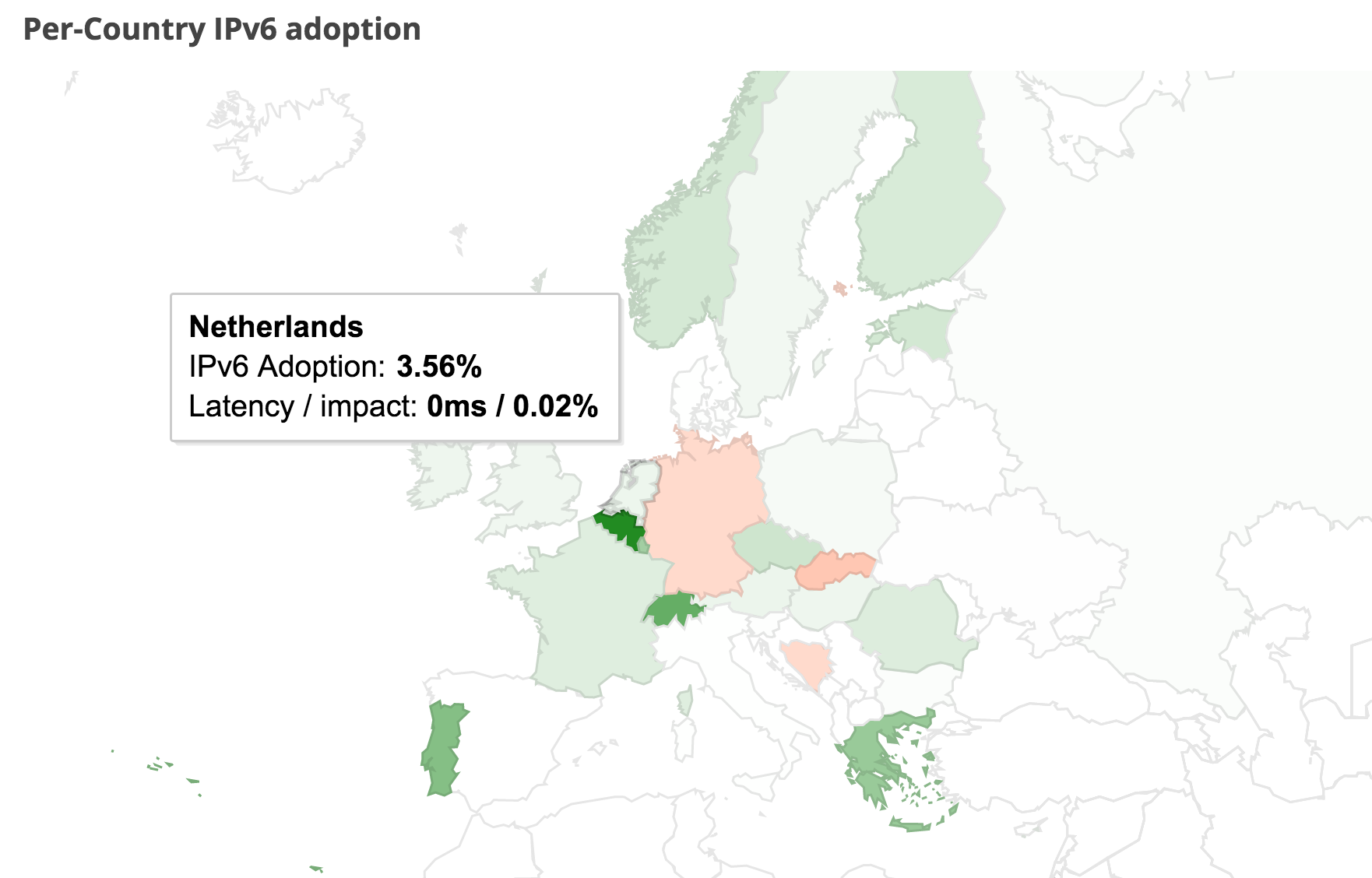
België is wereldwijd koploper met zo'n 45% en landen als Portugal en Griekenland zitten rond de 20%. Er zijn echter ook landen die nog onder de 1% blijven hangen.
Het hele verhaal bij Ars Technica: IPv6 celebrates its 20th birthday by reaching 10 percent deployment
Het is ook opgepikt door de AutomatiseringGids: Gebruik IPv6 na 20 jaar op 10 procent
Permalink - posted 2016-01-04
When I first started running IPv6 over BGP, I ran into an interesting problem. The Cisco router I was working on had four full BGP feeds over IPv4. But when did show ip bgp, I noticed the router had five copies of each prefix. One of these paths had a really weird next hop address and was marked as unreachable.
Turned out those were IPv4 prefixes learned over an IPv6 BGP session.
Read the article - posted 2016-03-18
One of the tiebreakers in the BGP best path selection algorithm is to prefer the path learned from a BGP speaker with the lowest BGP identifier. So how are BGP identifier selected when they're not configured explicitly?
I always forget whether it's the highest or the lowest IP address configured on a Cisco router. Turns out this is remarkably hard to find in Google, but if you know where to look it's in Cisco's IOS command reference:
Permalink - posted 2016-04-22
- If a loopback interface is configured, the router ID is set to the IP address of the loopback interface. If multiple loopback interfaces are configured, the router ID is set to the IP address of the loopback interface with the highest IP address.
- If no loopback interface is configured, the router ID is set to the highest IP address on a physical interface.